Can Emergency Contraception Cause Ovarian Cysts?
Nov 22, 2017
Emergency Contraception
Emergency contraception is also known as the morning after pill because you take it after unprotected sex to prevent pregnancy. It works by preventing ovulation so that contraception can’t take place.
It is exactly the same as taking the normal contraceptive pill but in higher concentration. People worry about the side effects of taking emergency contraception because of the high levels of hormones it involves. Many people worry that emergency contraception is the same as an abortion when it actually prevents the egg from being fertilised by a sperm.
There are concerns that stopping ovulation leads to ovarian cysts and ectopic pregnancies. Although people find they have ovarian cysts after taking emergency contraception it doesn’t necessarily mean that the medication caused them.
BROWSE EMERGENCY CONTRACEPTION OPTIONS

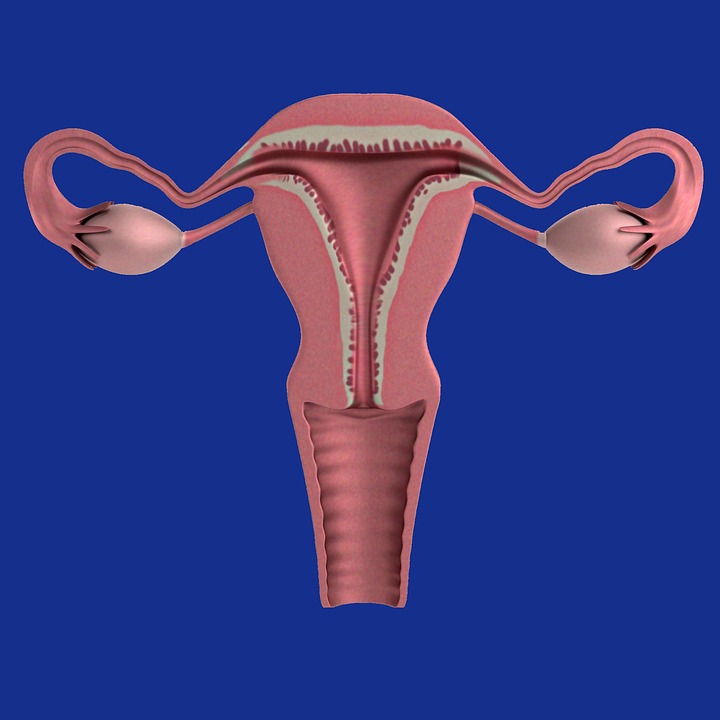
Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form in and around the ovaries. There are five types of ovarian cyst which form during the menstrual cycle. Ovarian cysts are not normally cancerous.
The two most common cysts are follicle and corpus luteum. Other types of cyst are; endometriomas, dermoids and cystadenomas. Small cysts produced by the ovaries cause polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
Follicle Cysts
Every month ovaries release an egg in a sac called a follicle. Normally the follicle breaks when the egg matures. A follicle cyst occurs when the egg is not released. The follicle continues to grow to form a cyst. This type of cyst generally lasts for three months without any noticeable symptoms.
Corpus Luteum Cysts
Corpus luteum cysts form after the follicle releases the egg. Normally the sack forms into a tiny mass of cells that produces hormones to help prepare for the next egg to be produced.
If the sack doesn’t get smaller it seals up and expands due to a buildup of fluid. Cysts like these grow up to 10 centimetres and can cause a degree of pain.
Medication taken to promote ovulation can sometimes be the cause of corpus luteum cysts. Endometriomas are caused by the condition endometriosis where the womb lining sheds outside the uterus.
Cystadenomas are fluid filled sacks that can grow quite large while dermoids are present from birth and symptomless. Ovarian cysts are normally benign (not cancerous) ovarian cancer is caused by malignant cysts.
Causes
Ovarian cysts occur in 8% of premenopausal women and are less likely after the menopause. Ovarian cancer is more likely to occur in women who have cysts after they have had the menopause.
The main causes of ovarian cysts are; endometriosis, pregnancy, hormonal imbalance and pelvic infections. Medication used to promote ovulation is a common cause of ovarian cysts while the pill and emergency contraception prevent ovulation from occurring.
Women who take this form of contraception are less likely to get ovarian cancer because ovulation is delayed. All forms of hormonal contraception except for the mini pill provide this type of protection.
Treatments
Generally, ovarian cysts remain hidden until they begin to cause pain in the pelvis, unexplained weight gain, painful periods and unusual vaginal bleeding. A pelvic examination, ultrasound, pregnancy test, hormone test and a blood test are used to determine if you have a cyst.
Most cysts go away after a few menstrual cycles but some are more stubborn and require surgical intervention to remove them. Surgery is determined by the effect the cyst has on your health. If you suffer severe pain, vomiting, fever and breathlessness your cyst may have ruptured and it will need removing.
There are two types of surgery used to remove a cyst laparoscopy or laparotomy the former is less invasive and the latter is used if the cyst is cancerous and the ovaries need removing. Most ovarian cysts are not cancerous. Doctors prescribe the contraceptive pill to help avoid ovarian cysts from occurring.
Emergency Contraception and Ovarian Cysts
Emergency contraception works in exactly the same way as the contraceptive pill. It prevents pregnancy by stopping ovulation occurring. There are concerns that emergency contraception causes ovarian cysts because of the high level of hormones involved.
Doctors prescribe the contraceptive pill to prevent ovulation and reduce the chances of having ovarian cysts. Emergency contraception is made up of the same components as the regular contraceptive pill so will not increase your chances of having ovarian cysts.
EllaOne and Levonelle are popular brands of emergency contraception. EllaOne can be taken up to five days after unprotected sex while Levonelle is three days.
Emergency contraception is taken as soon as possible after unprotected sex is more effective. If you have any concerns about emergency contraception and ovarian cysts you should visit your doctor who will be able to give you the best advice.





























































 Account
Account